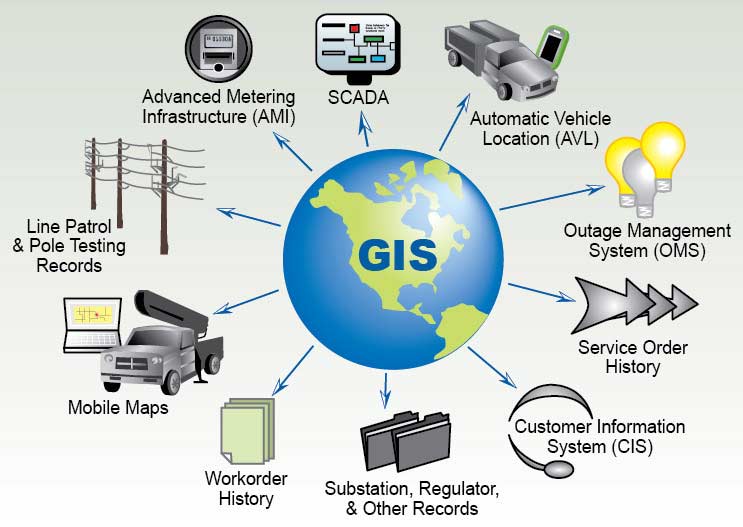
GIS Application
GIS (Geographic Information System) applications leverage GIS technology across various sectors to capture, store, analyze, and present geospatial data. By effectively using spatial information, these applications not only provide comprehensive insights but also significantly support informed decision-making and robust spatial analysis. In addition, in fields such as urban planning, emergency management, agriculture, and healthcare, GIS consistently plays a pivotal role in optimizing processes and allocating resources. For instance, whether it involves mapping city infrastructure, monitoring environmental changes, or planning transportation networks, GIS contributes substantially to efficient solutions and sustainable practices.
Moreover, due to their inherent adaptability, GIS applications have quickly become essential tools that support industries ranging from business and marketing to defense and education. Furthermore, the ongoing convergence of technology and geography within GIS applications continues to redefine how organizations harness spatial data for strategic planning and operational efficiency. Consequently, by actively embracing GIS technology, organizations not only empower themselves to make data-driven decisions that drive progress and foster innovation but also enhance their competitive edge in the marketplace.
Ultimately, this seamless integration of technology and geospatial data improves productivity and substantially boosts overall organizational effectiveness. Therefore, organizations that effectively leverage GIS are far better positioned to respond to challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities in a rapidly changing environment. In addition, by adopting GIS technology, organizations can streamline operations, enhance collaboration across multiple departments, and ultimately increase their responsiveness to market demands. In summary, adopting GIS technology is not merely beneficial; rather, it is absolutely essential for organizations aiming to thrive in today’s data-driven landscape. Indeed, GIS both fosters innovation and drives strategic growth, ensuring that organizations remain at the forefront of their respective industries.
Wide Range Of GIS Applications
Urban Planning:
GIS supports urban planning through land-use analysis, infrastructure development, and zoning. This approach leads to smarter decisions for city growth.Environmental Monitoring:
In environmental sciences, GIS monitors natural resources and biodiversity. It also assesses changes and supports conservation efforts.Public Health:
GIS is crucial for disease mapping and tracking illness spread. It helps optimize healthcare resources and reveals health patterns.Emergency Management:
During disasters, GIS offers real-time mapping and evacuation planning. This enhances the efficiency of response and recovery efforts.Transportation and Logistics:
GIS analyzes traffic and plans routes. It reduces congestion and travel times while improving overall transportation efficiency.Agriculture and Precision Farming:
In agriculture, GIS optimizes crop yields. It analyzes soil conditions, irrigation, and crop health for better farming practices.Telecommunications:
GIS aids telecommunications by supporting network planning and site selection. It ensures effective communication infrastructure.Natural Resource Management:
GIS helps manage resources like forests and water sustainably. It balances use and conservation for informed decision-making.